
" Computational assessment of the DeepWind aerodynamic performance with different blade and airfoil configurations,"Īpplied Energy, Elsevier, vol. Bedon, Gabriele & Schmidt Paulsen, Uwe & Aagaard Madsen, Helge & Belloni, Federico & Raciti Castelli, Marco & Benini, Ernesto, 2017." Near wake flow analysis of a vertical axis wind turbine by stereoscopic particle image velocimetry," " Performance improvement of a vertical axis wind turbine by comprehensive assessment of an airfoil family,"Įnergy, Elsevier, vol. Chen, Jian & Chen, Liu & Xu, Hongtao & Yang, Hongxing & Ye, Changwen & Liu, Di, 2016." Wind tunnel experiments and Delayed Detached Eddy Simulation of a three-bladed micro vertical axis wind turbine,"
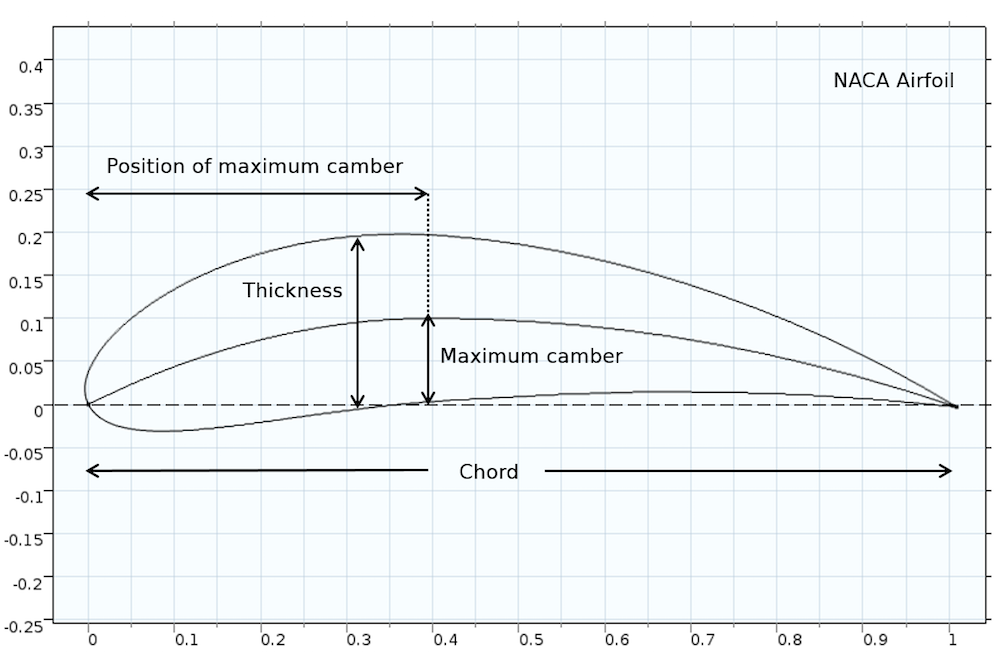
AIRFOIL PROFILE SERIES
" Study on start-up characteristics of H-Darrieus vertical axis wind turbines comprising NACA 4-digit series blade airfoils,"Įnergy, Elsevier, vol.
Asr, Mahdi Torabi & Nezhad, Erfan Zal & Mustapha, Faizal & Wiriadidjaja, Surjatin, 2016. " Effect of airfoil profile on aerodynamic performance and economic assessment of H-rotor vertical axis wind turbines,"Įnergy, Elsevier, vol. Jafari, Mohammad & Razavi, Alireza & Mirhosseini, Mojtaba, 2018. " Effect of solidity on the performance of variable-pitch vertical axis wind turbine,"Įnergy, Elsevier, vol. " Theoretical Modeling of Vertical-Axis Wind Turbine Wakes,"Įnergies, MDPI, vol. " Effect of airfoil and solidity on performance of small scale vertical axis wind turbine using three dimensional CFD model,"Įnergy, Elsevier, vol. Arun & Sivanandan, Hrishikesh & Giri, Abhijit & Vasudevan, Madhavan & Mugundhan, Vivek & Velamati, Ratna Kishore, 2017. " Numerical Investigation on the Effects of Airfoil Leading Edge Radius on the Aerodynamic Performance of H-Rotor Darrieus Vertical Axis Wind Turbine,"Įnergies, MDPI, vol. Chenguang Song & Guoqing Wu & Weinan Zhu & Xudong Zhang & Jicong Zhao, 2019. " Performance investigation of H-rotor Darrieus turbine with new airfoil shapes,"Įnergy, Elsevier, vol. " The Darrieus wind turbine: Proposal for a new performance prediction model based on CFD,"Įnergy, Elsevier, vol. Raciti Castelli, Marco & Englaro, Alessandro & Benini, Ernesto, 2011. " Active flow control for power enhancement of vertical axis wind turbines: Leading-edge slot suction," Mathematical Problems in Engineering, Hindawi, vol. " Influence of Thickness Variation on the Flapping Performance of Symmetric NACA Airfoils in Plunging Motion," " On the accuracy of turbulence models for CFD simulations of vertical axis wind turbines,"Įnergy, Elsevier, vol. Rezaeiha, Abdolrahim & Montazeri, Hamid & Blocken, Bert, 2019. In general, reducing I from the default value of 6.0 to 4.5 is found to increase the turbine CP. When λ reduces from 3.0 to 2.5, the optimal airfoil changes from NACA0018–4.5/2.75 to NACA0024–4.5/3.5, that is increasing the maximum thickness from 18%c to 24%c and shifting its position from 27.5%c to 35%c, while the leading-edge radius index, I, remains 4.5. The results show that the three shape defining parameters have a fully coupled impact on the turbine power and thrust coefficients. 
The simulations are verified and validated with three experiments. The analysis is based on 252 high-fidelity transient CFD simulations of 126 identical airfoil shapes. The present study performs a combined analysis of three shape defining parameters, namely the airfoil maximum thickness and its position as well as the leading-edge radius, to reveal the overall design space. The optimal airfoil shape for VAWTs at low λ, where dynamic stall is present, has not yet been studied in the literature, therefore, the present study addresses this gap by focusing on this regime to serve as a step towards designing morphing airfoils for VAWTs by identifying the optimal airfoil shape at low λ. Morphing airfoils can be a potential solution by modifying the airfoil shape to optimal at each λ. At relatively high wind speeds, which are promising due to high wind power potential, VAWTs operate at low λ with poor power coefficient. The current design of vertical axis wind turbines (VAWTs) suffers from inevitable change in tip speed ratio, λ, in variant wind conditions due to fixed rotor speed.






 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
